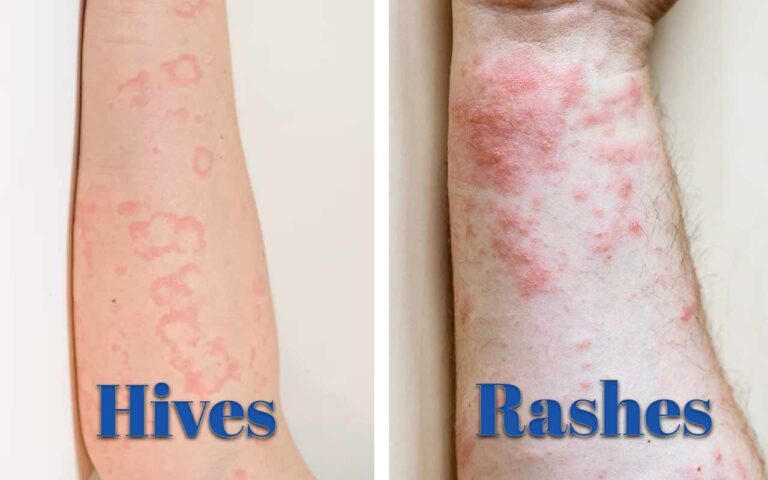
Rash and hives are common skin conditions that can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. They can cause itching, redness, and swelling of the skin. They can also form blisters or crusts that may ooze or bleed.
Rash and hives are not the same, but they can look similar and have similar symptoms. However, they have different causes and treatments. Therefore, it is important to know how to tell the difference between rash and hives and how to treat them naturally.
In this article, we will explain the difference between rash and hives by their appearance, symptoms, and causes. We will also share with you some effective natural remedies and tips to soothe your skin and heal your rash and hives.
Table of Contents
What is Rash?
A rash is a general term that refers to any change in the color, texture, or appearance of the skin. A rash can be localized or widespread, acute or chronic, mild or severe. A rash can have various shapes, sizes, and patterns.
A rash is a common skin condition that causes redness, itching, and inflammation. It can affect any part of the body, but some areas are more prone to it than others. One of these areas is behind the ear, where the skin is sensitive and moist.
If you have a red, itchy, and flaky skin behind your ears, you may have rash behind the ears. This is a common skin condition that can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. A rash behind the ear can be caused by various factors, such as allergies, infections, eczema, or psoriasis.
It can be treated with home remedies, such as tea tree oil or aloe vera gel, or with medications, such as antihistamines or corticosteroids. To learn more about this condition, read this article: How to get rid of a rash behind the ear with natural remedies.
A rash can be caused by various factors, such as:
- Allergic reaction, such as to food, medication, or insect bites
- Infection, such as by bacteria, virus, fungus, or parasite
- Irritation, such as by chemicals, metals, or plants
- Inflammation, such as by dermatitis, eczema, or psoriasis
- Autoimmune disorder, such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, or scleroderma
- Hormonal imbalance, such as by pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid disorder
- Stress, anxiety, or emotional distress
- Genetic disorder, such as by albinism, neurofibromatosis, or tuberous sclerosis
Some common types of rash include:
- Contact dermatitis, which is a skin reaction to an irritant or an allergen, such as earrings, cosmetics, or poison ivy
- Atopic dermatitis, which is a chronic form of eczema that causes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin
- Seborrheic dermatitis, which is a skin condition that causes oily, scaly, and red patches on the scalp, face, or chest
- Impetigo, which is a bacterial infection that causes yellow, crusty, and contagious sores on the skin
- Ringworm, which is a fungal infection that causes scaly, red, and circular patches on the skin
- Shingles, which is a viral infection that causes painful, blistering, and band-like rashes on one side of the body
- Scabies, which is a parasitic infection that causes intense itching and burrows on the skin
- Lichen planus, which is an autoimmune disorder that causes purple, flat, and itchy bumps on the skin
- Granuloma annulare, which is a skin condition that causes red, raised, and ring-shaped lesions on the skin
What are the symptoms and causes of rashes?
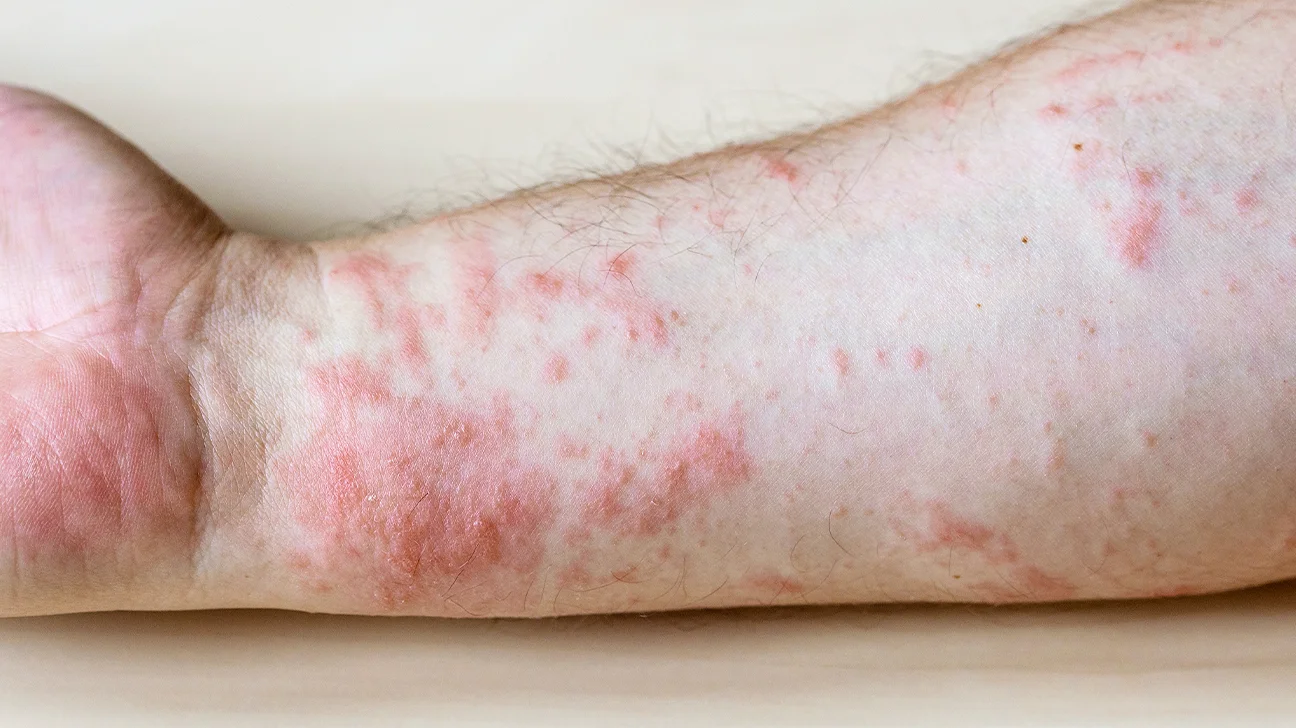
A rash is a change in the color, texture, or appearance of the skin. It can cause itching, pain, or warmth. It can also form blisters, scales, or bumps. A rash can affect a small or large area of the skin, depending on the cause.
Rashes can have many different causes, such as allergies, infections, irritations, or diseases. Some of the common causes of rashes are:
- Contact dermatitis, which is a skin reaction to something that touches the skin, such as soap, jewelry, or plants
- Allergic eczema, which is a type of dermatitis that is caused by an allergic reaction to something in the environment, such as dust, pollen, or animal dander
- Psoriasis, which is a chronic skin condition that causes red, scaly, and itchy patches on the skin
- Lupus, which is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and damage to various organs, including the skin
- Fifth disease, which is a viral infection that causes a red rash on the face, arms, and legs, especially in children
- Impetigo, which is a bacterial infection that causes yellow, crusty, and contagious sores on the skin
- Bug bites, which are skin reactions to the saliva or venom of insects, such as fleas, bed bugs, or mosquitoes
- Cellulitis, which is a bacterial infection that causes redness, swelling, and pain in the skin and underlying tissues
How to treat rashes effectively
The treatment of rashes depends on the cause and severity of the rash. Some mild rashes may go away on their own or with home remedies, such as those used for hives. However, some rashes may require medical attention and prescription medication.
Some of the possible treatments for rashes are:
- Soaking in a colloidal oatmeal bath, which is a mixture of finely ground oatmeal and water that can help soothe and moisturize the skin
- Applying topical corticosteroids to the area, which are creams or ointments that can help reduce inflammation and itching
- Taking oral antihistamines, which are pills or syrups that can help block the histamine that causes allergic reactions and itching
- Applying topical retinoids to the area, which are creams or gels that can help normalize the growth and shedding of skin cells
- Applying aloe vera to the area, which is a gel from a plant that can help heal the skin and prevent infection
- Taking oral or injected prescription medications, such as antibiotics, immunosuppressants, or biologics, which can help treat the underlying cause of the rash, such as infection, autoimmune disorder, or severe inflammation
What are Hives?
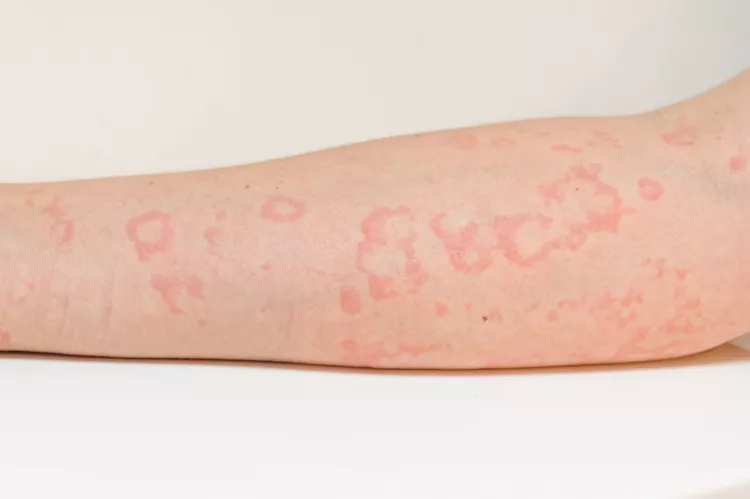
Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, itchy, and red bumps or welts on the skin. They can appear anywhere on the body and vary in size, shape, and number. They can last for a few hours or a few days, or they can come and go for weeks or months.
Hives are caused by the release of histamine, a chemical that causes inflammation and swelling of the skin. Histamine is released by the immune system in response to an allergen, a substance that the body is sensitive to.
Some common allergens that can cause hives include:
- Food, such as nuts, eggs, shellfish, or strawberries
- Medication, such as antibiotics, aspirin, or ibuprofen
- Insect bites or stings, such as by bees, wasps, or mosquitoes
- Animal dander, such as by cats, dogs, or horses
- Pollen, dust, or mold
- Latex, rubber, or plastic
However, sometimes the cause of hives is unknown, which is called idiopathic urticaria. This can be due to a hidden infection, a chronic disease, or a genetic predisposition.
Some common types of hives include:
- Acute urticaria, which is hives that last for less than six weeks and are usually caused by an allergic reaction
- Chronic urticaria, which is hives that last for more than six weeks and are usually caused by an unknown factor
- Physical urticaria, which is hives that are triggered by physical stimuli, such as heat, cold, pressure, or exercise
- Angioedema, which is a severe form of hives that affects the deeper layers of the skin and causes swelling of the face, lips, tongue, throat, or genitals
What are the symptoms and causes of hives?
How do hives look and feel?
Hives are raised, red, and itchy bumps or welts on the skin. They can appear anywhere on the body and vary in size and shape. Sometimes, they can join together and form large, swollen patches of skin. The skin around the hives may also be inflamed and irritated.
Hives can cause mild or severe itching that can last for a few minutes or several hours. The itching may start before the hives appear or at the same time. Hives can also come and go quickly or persist or recur for a long time.
What triggers hives?
Hives are caused by the release of histamine, a chemical that makes the blood vessels leak fluid into the skin. Histamine is released by the immune system when it reacts to something that it thinks is harmful, such as an allergen.
Allergies are the most common cause of hives. You can get hives if you are allergic to something that you eat, drink, touch, or breathe, such as:
- Food, such as nuts, eggs, shellfish, or strawberries
- Medication, such as antibiotics, aspirin, or ibuprofen
- Insect bites or stings, such as by bees, wasps, or mosquitoes
- Animal dander, such as by cats, dogs, or horses
- Pollen, dust, or mold
- Latex, rubber, or plastic
However, not all hives are caused by allergies. Some other possible triggers are:
- Extreme temperatures, such as heat or cold
- Sunlight or artificial light
- Stress, anxiety, or nervousness
- Certain bacterial or viral infections, such as strep throat or urinary tract infections
Sometimes, the cause of hives is unknown. This is called idiopathic urticaria. It may be due to a hidden infection, a chronic disease, or a genetic factor.
How to treat hives effectively
Hives are itchy, red, and swollen bumps on the skin that can appear due to an allergic reaction or other triggers. They may go away on their own, but sometimes they can persist or recur for a long time.
The best way to treat hives is to avoid the allergen or the factor that causes them. However, this may not be easy or possible in some cases.
If you have hives, you can try some natural remedies and over-the-counter medications to relieve your symptoms and speed up the healing process. Some of these are:
- Taking oral antihistamines to reduce the itching and swelling
- Applying cortisone cream to the area to reduce the inflammation and redness
- Applying calamine lotion to the area to soothe the skin and prevent scratching
- Soaking the area with a cool compress of witch hazel to shrink the blood vessels and ease the irritation
- Using a cold water compress on the area to numb the pain and lower the temperature
- Wearing loose clothing that doesn’t rub or scratch the skin
- Avoiding sun exposure that can worsen the hives or trigger new ones
Hives can vary in duration and severity. Some hives may last for a few hours or days, while others may last for weeks or months.
If you have chronic or severe hives that don’t respond to the home treatments, you may need to see a doctor for a stronger prescription. Some of the medications that your doctor may prescribe are:
- Prescription antihistamines that are more potent and longer-lasting than the over-the-counter ones
- Oral corticosteroids that suppress the immune system and reduce the inflammation and swelling
- Biologic drugs that target specific molecules involved in the allergic response and prevent the release of histamine
- Epinephrine injection that is used in emergency situations when the hives cause a life-threatening reaction, such as anaphylaxis
Hives can be a frustrating and uncomfortable condition, but they can be treated effectively with the right methods and medications. If you have hives, try to identify and avoid the triggers, use the natural remedies and over-the-counter medications, and consult your doctor if you need a stronger prescription.
How to Tell the Difference Between Rash and Hives
Rash and hives can look similar and have similar symptoms, but they have different causes and treatments. Therefore, it is important to know how to tell the difference between rash and hives.
Here are some ways to tell the difference between rash and hives:
- Appearance: Rash can have various shapes, sizes, and patterns, while hives are usually round, oval, or irregular. Rash can be flat, raised, or scaly, while hives are always raised and smooth. Rash can be localized or widespread, while hives are usually widespread and symmetrical.
- Symptoms: Rash can cause itching, burning, pain, or bleeding, while hives usually cause only itching. Rash can be accompanied by other symptoms, such as fever, headache, or joint pain, while hives are usually isolated to the skin. Rash can last for days, weeks, or months, while hives usually last for hours or days.
- Causes: Rash can be caused by various factors, such as infection, irritation, inflammation, or autoimmune disorder, while hives are usually caused by an allergic reaction or an unknown factor. Rash can be diagnosed by a skin scraping, biopsy, or culture test, while hives can be diagnosed by an allergy test or a blood test.
| Feature | Rash | Hives |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Varies in shapes, sizes, and patterns | Usually round, oval, or irregular |
| Texture | Flat, raised, or scaly | Always raised and smooth |
| Distribution | Localized or widespread | Usually widespread and symmetrical |
| Symptoms | Itching, burning, pain, or bleeding | Primarily itching |
| Additional symptoms | Fever, headache, joint pain | Usually limited to the skin |
| Duration | Days, weeks, or months | Hours or days |
| Causes | Infection, irritation, inflammation, autoimmune disorder | Allergic reaction, unknown factor |
| Diagnosis | Skin scraping, biopsy, or culture test | Allergy test, blood test |
| Image |
Key takeaways
While both hives and rashes can cause skin irritation, they have distinct characteristics. Here’s a quick guide to help you differentiate between them:
Appearance:
- Rashes: Vary in shape, size, and texture, often having flat, raised, or scaly patches.
- Hives: Typically round or oval, raised bumps with a smooth surface.
Symptoms:
- Rashes: Can cause itching, burning, pain, and even bleeding.
- Hives: Primarily cause intense itching.
Duration:
- Rashes: Can persist for days, weeks, or even months.
- Hives: Typically last for hours or days, disappearing and reappearing in new locations.
Causes:
- Rashes: Triggered by various factors like infections, irritants, inflammatory conditions, and autoimmune disorders.
- Hives: Primarily arise from allergic reactions, but the exact cause can sometimes be unknown.
Diagnosis:
- Rashes: Often diagnosed through skin tests, biopsies, or culture tests.
- Hives: Diagnosed using allergy or blood tests.
- Hives are a type of rash, but not all rashes are hives.
- Hives are often more widespread and symmetrical than rashes.
- Hives typically resolve quickly, while rashes can last for longer.
- Hives are usually caused by allergies, while rashes have a broader range of potential causes.
- Treatment for hives and rashes varies depending on the underlying cause.